** nest js sample 링크에서 어떻게 사용하는지 참조 가능
1. 터미널에서 git clone + 해당 코드 주소(https://github.com/nestjs/nest.git) 넣고
그리고 cd nest/ => cd sample/ => code .
let num_list:number[] = [1,2,3]
let myName = "dahan"
타입을 지정안해도 알아서 string으로 파악되지만
보통 대부분 ts를 사용하는 사람들은
let myName:string = "dahan"이런식으로 지정해서 사용 함
타입스크립트 사용하려면
npm i -g typescript
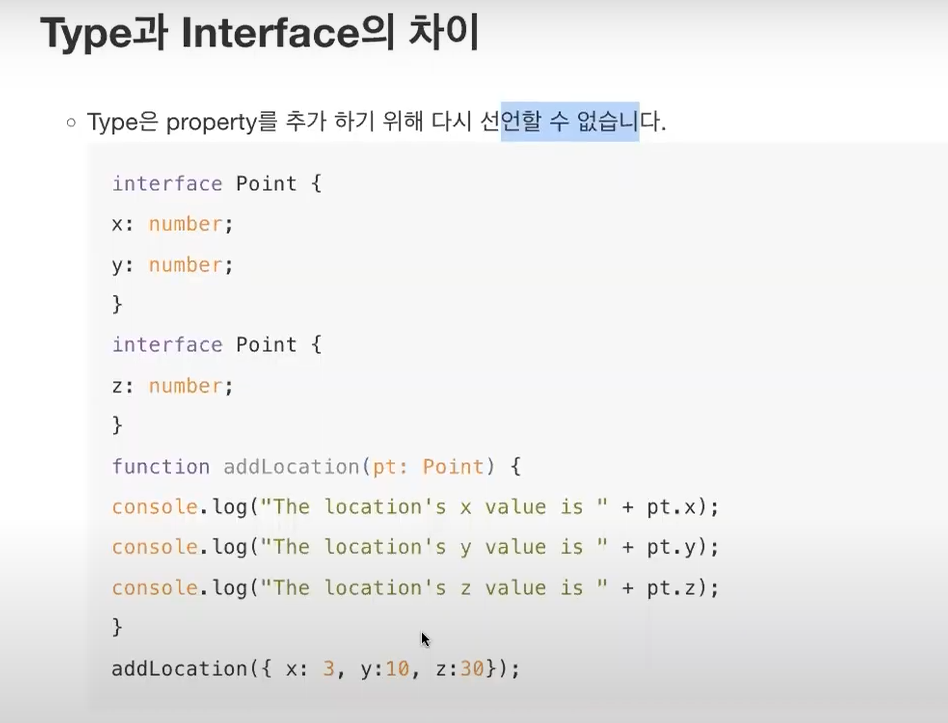
* Interface는 추가하기 위해 다시 선언 가능

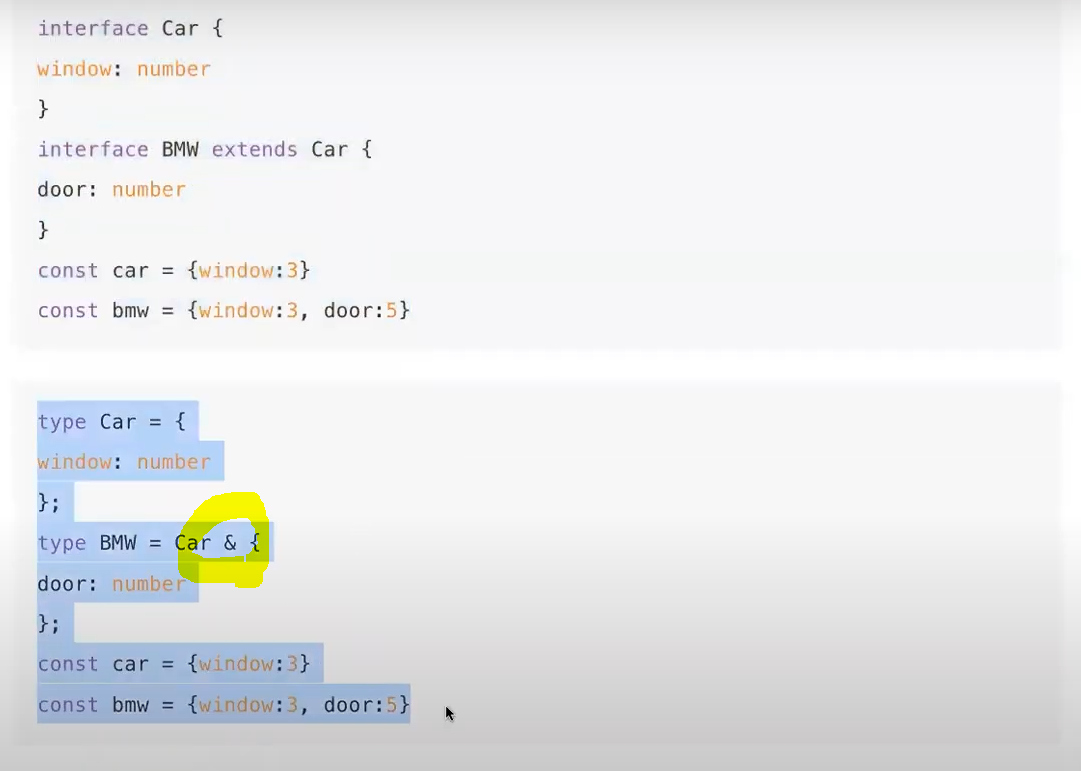
* 상속의 방법이 다름
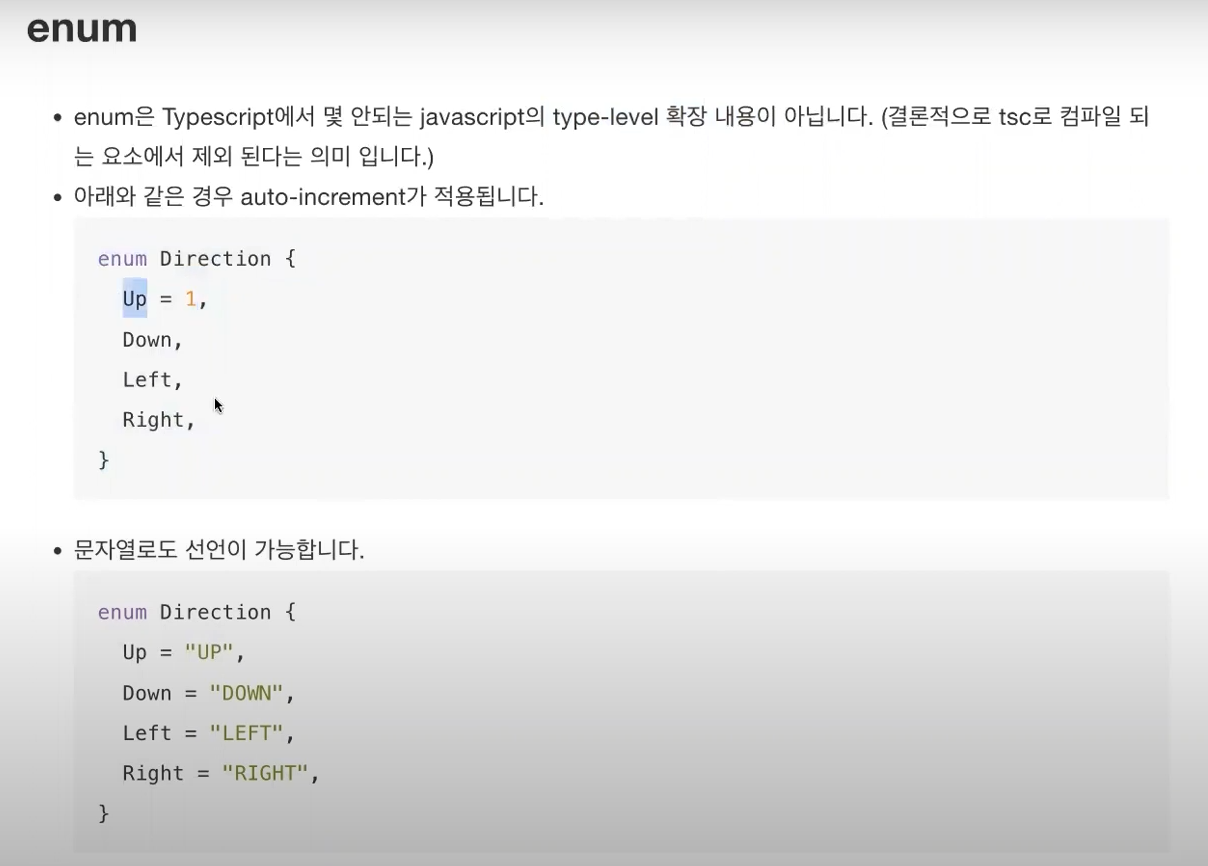
* enum
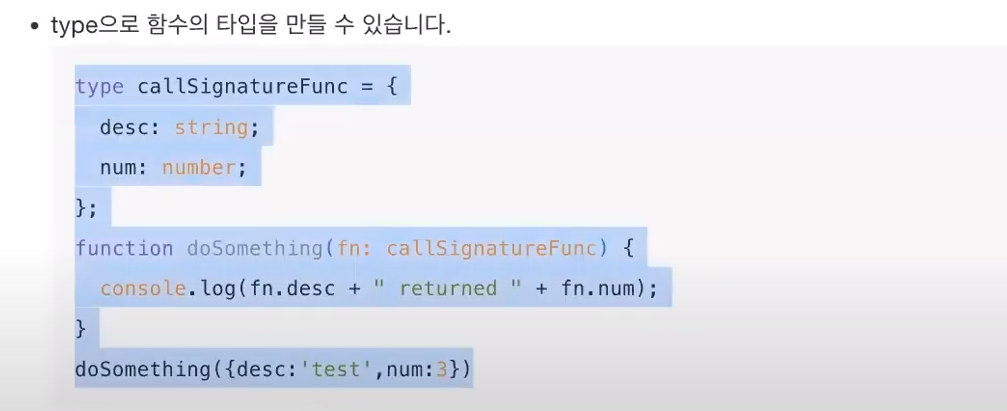
* 함수 ( 잘 이해 안 감 / 다시 이해하기 32:20)


* call signature
* Construct Signatures

* Class
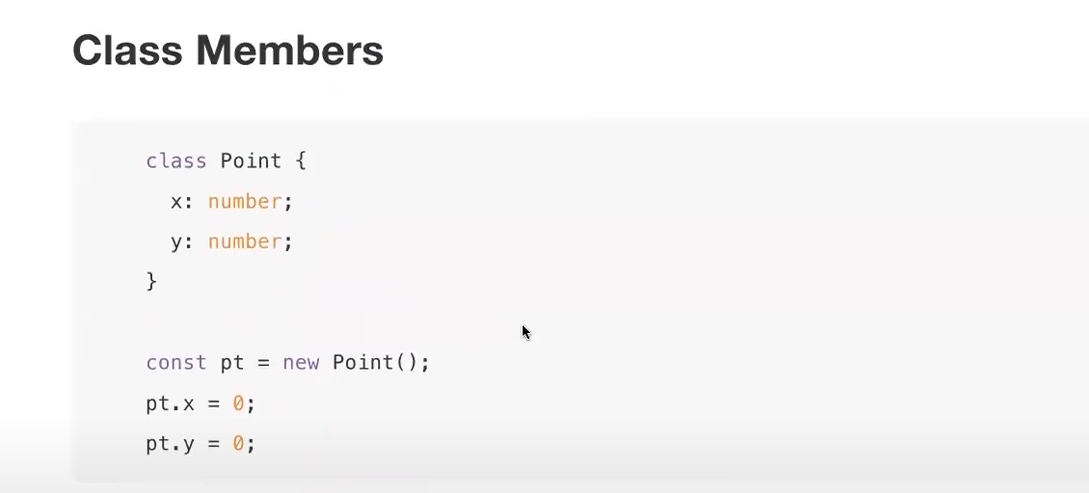
console.log(pt)
= 결과값 : Point { x: 0, y: 0 }

console.log(`${pt.x}, ${pt.y}`);
= 결과값 : 0, 0
* 생성자 활용
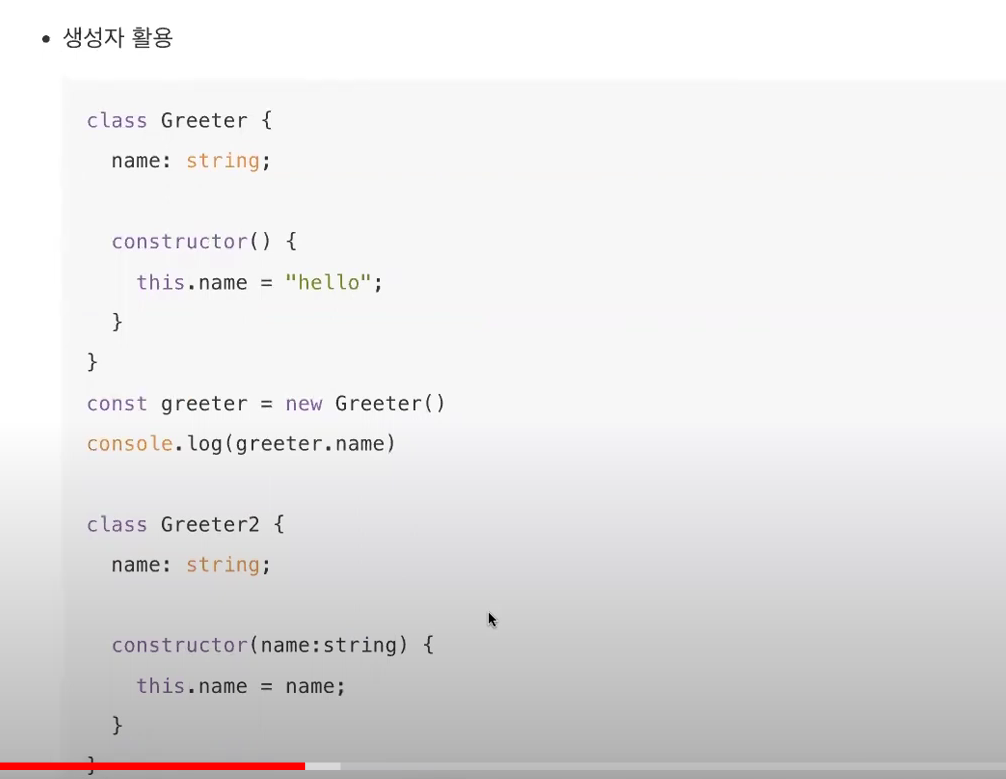
= 결과값: hello
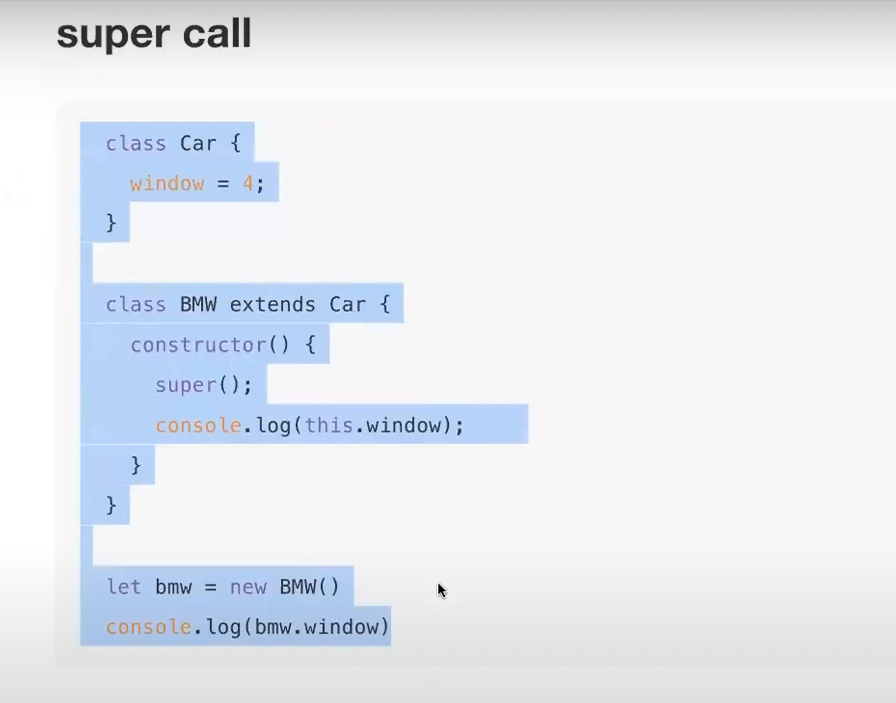
* super call
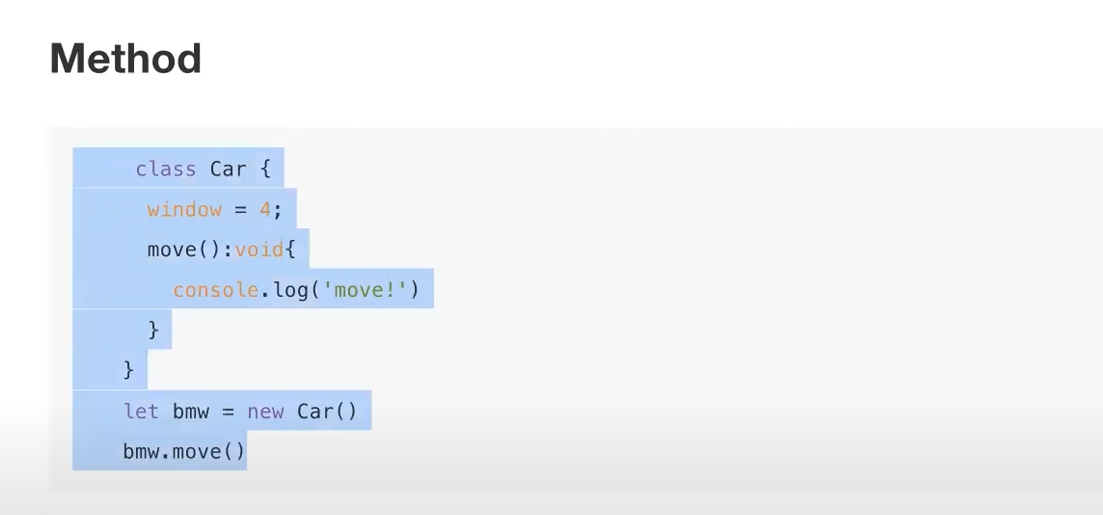
* Method
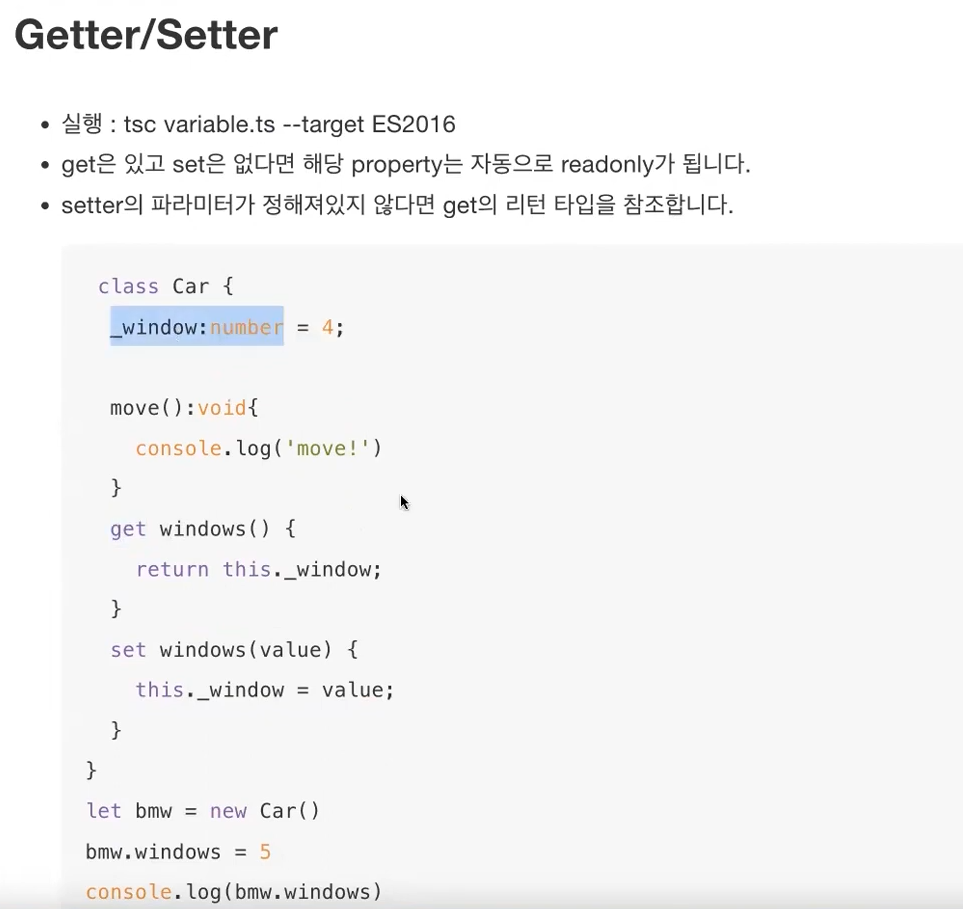
* Getter/Setter
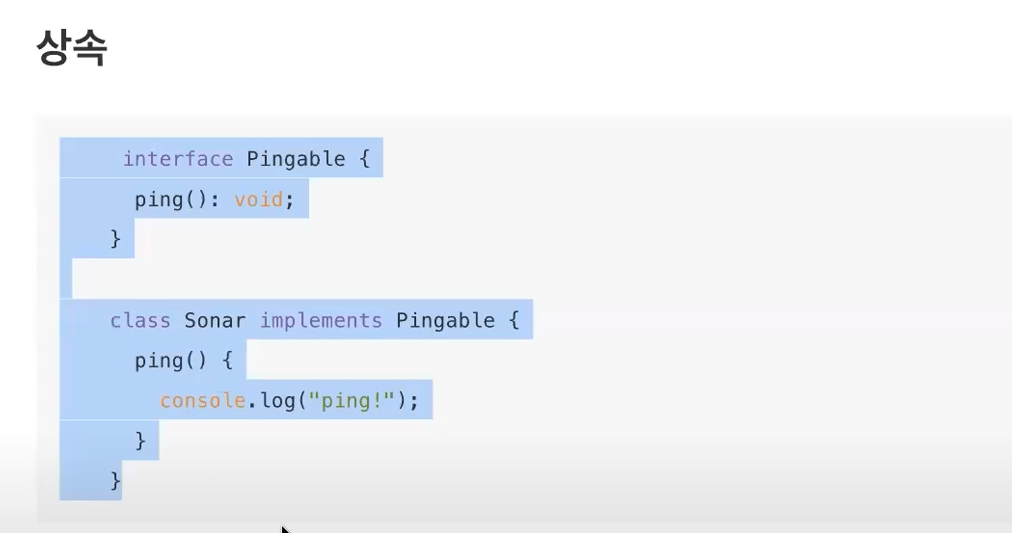
* 상속
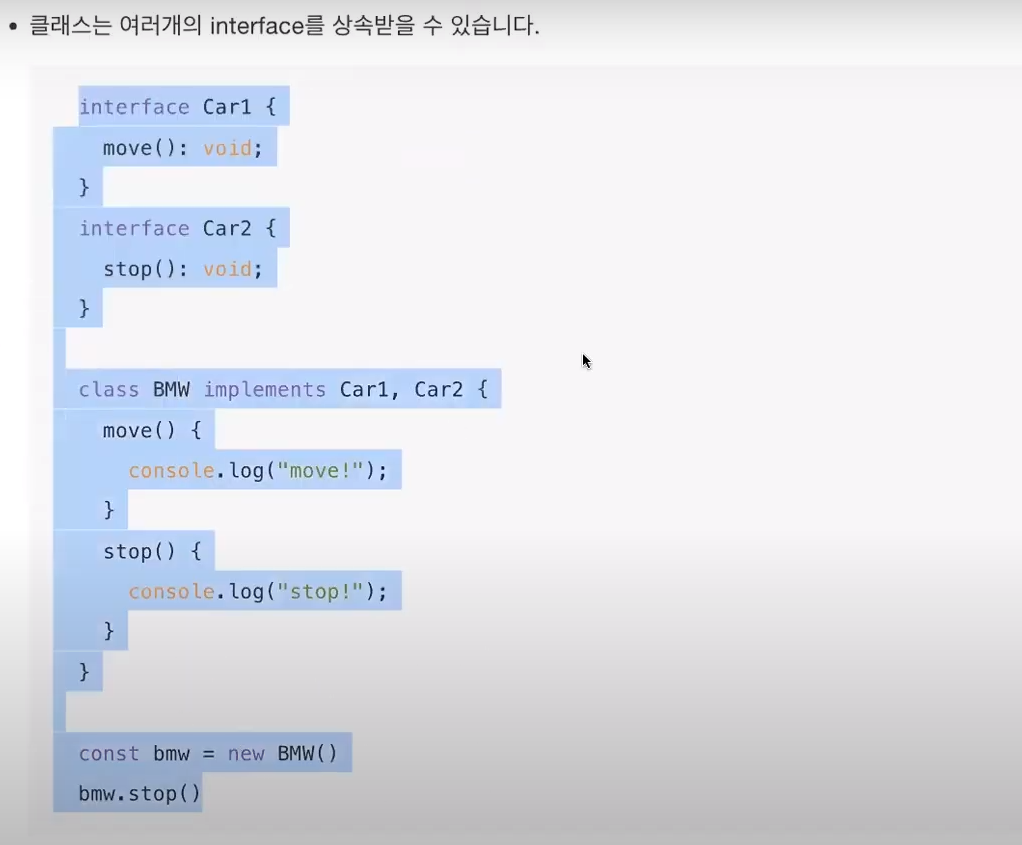
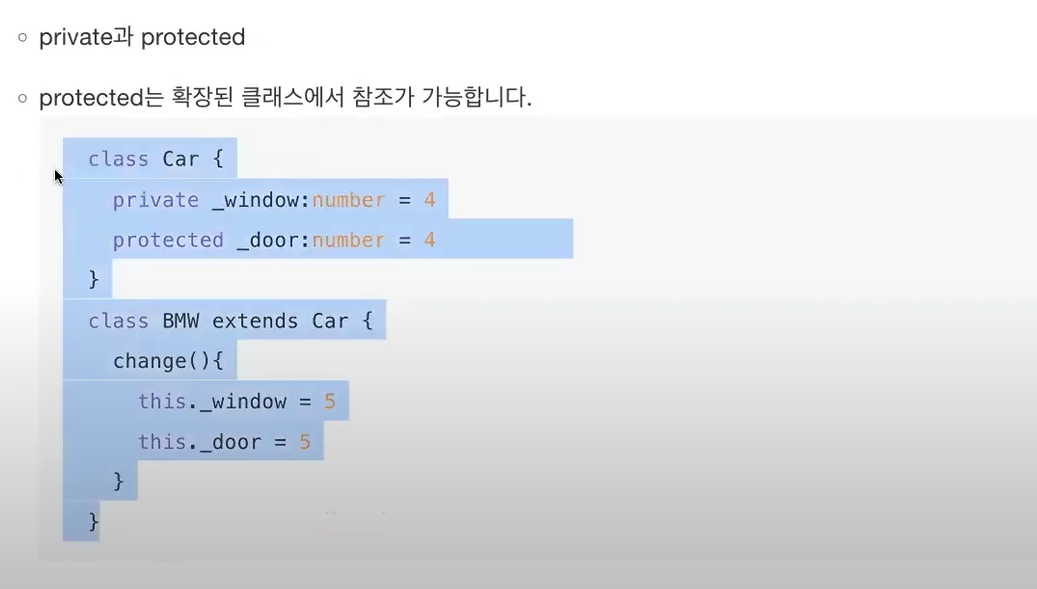
* Member Visiblity

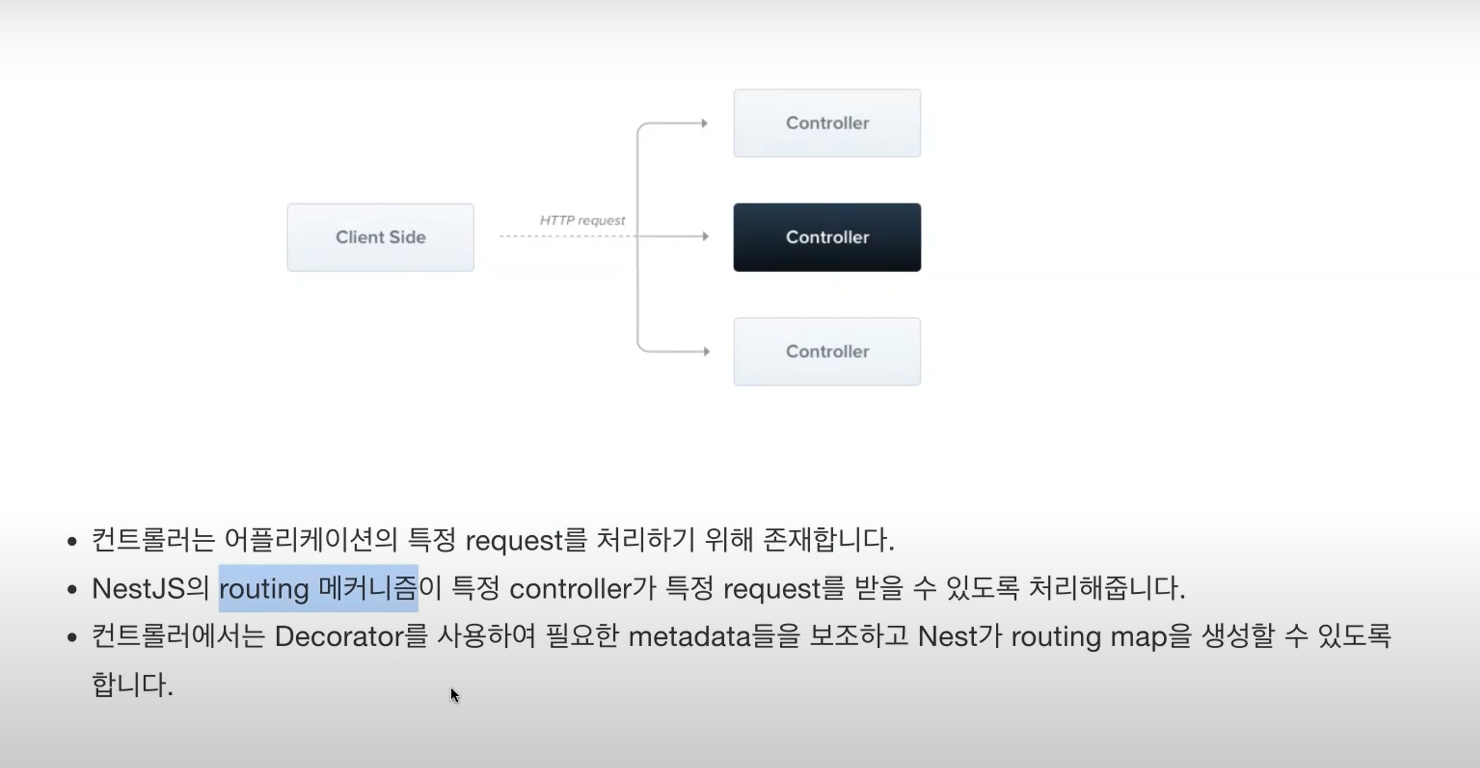
* Controller
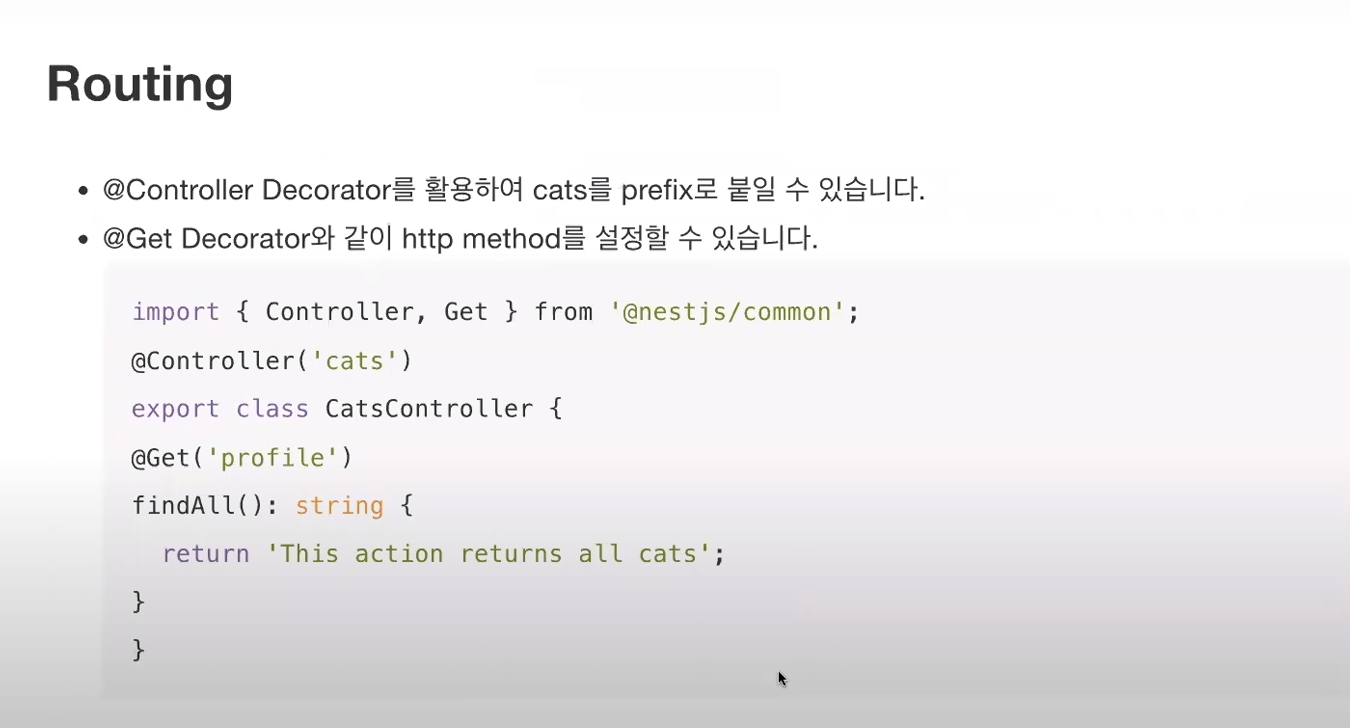
* Routing
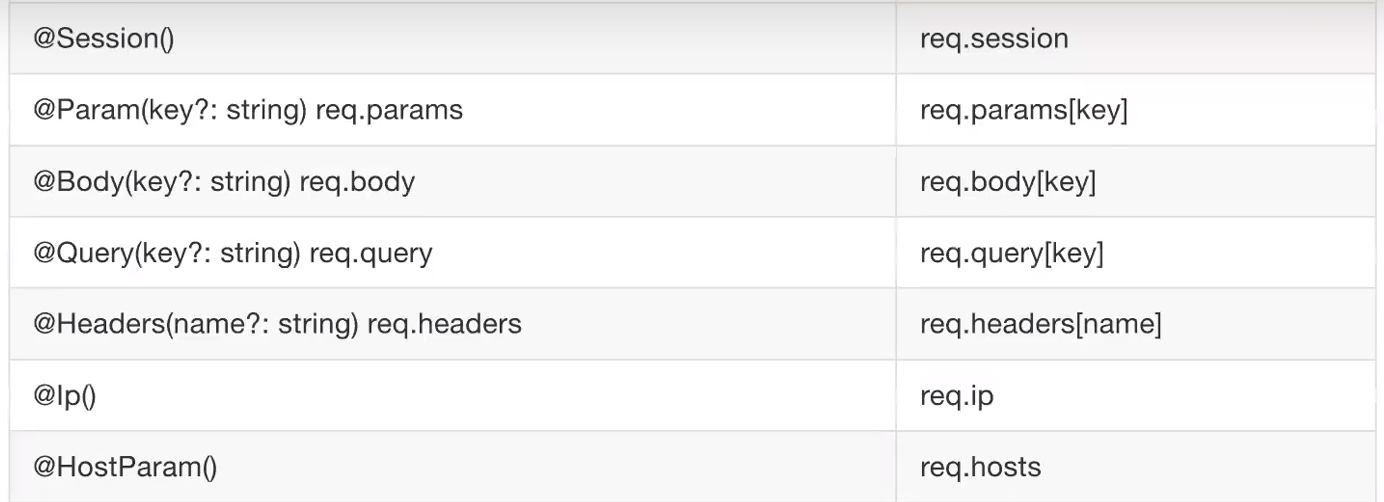
* Request Object


* Status code

* Header

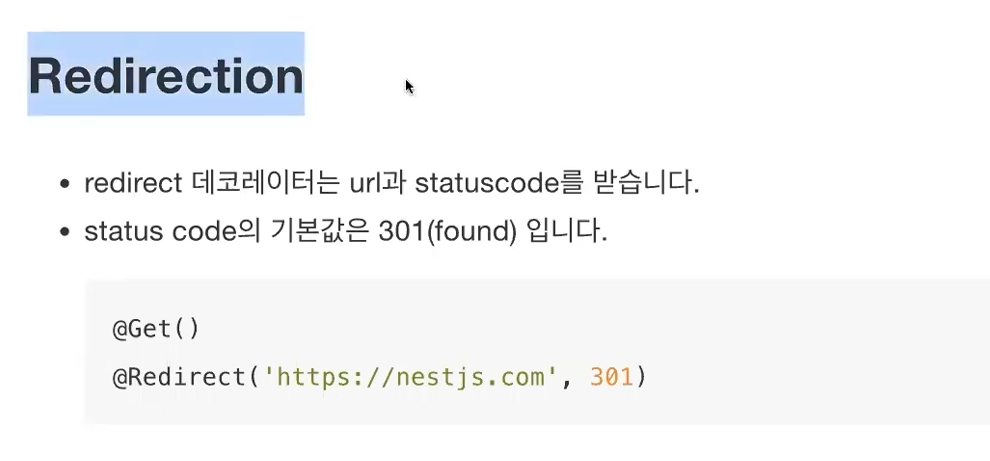
* Redirection
* Route Parameter

---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Controller 끝
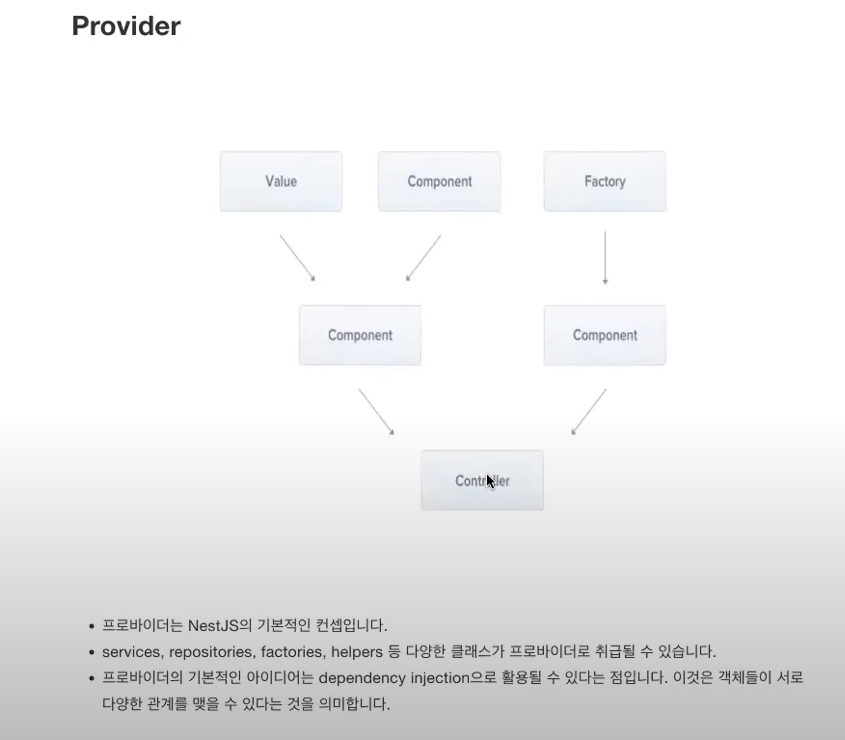
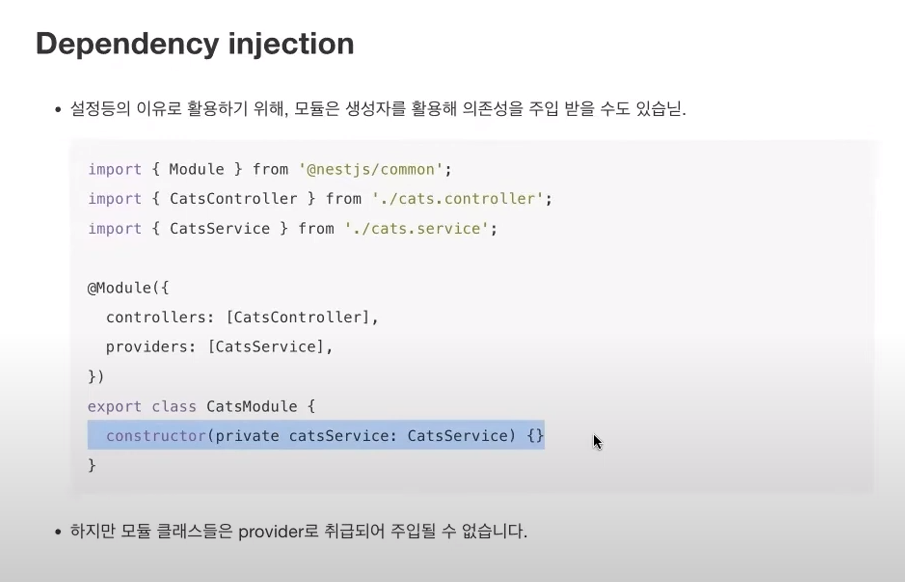
* Provider

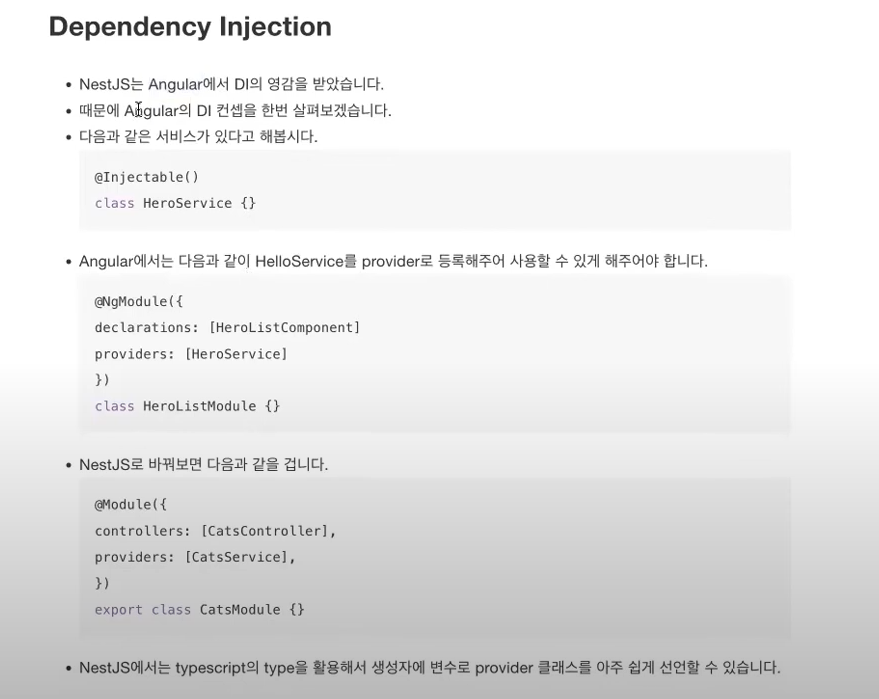
* Dependency Injection
* Scopes / Custom Providers


* Property-based injection

* Provider registration
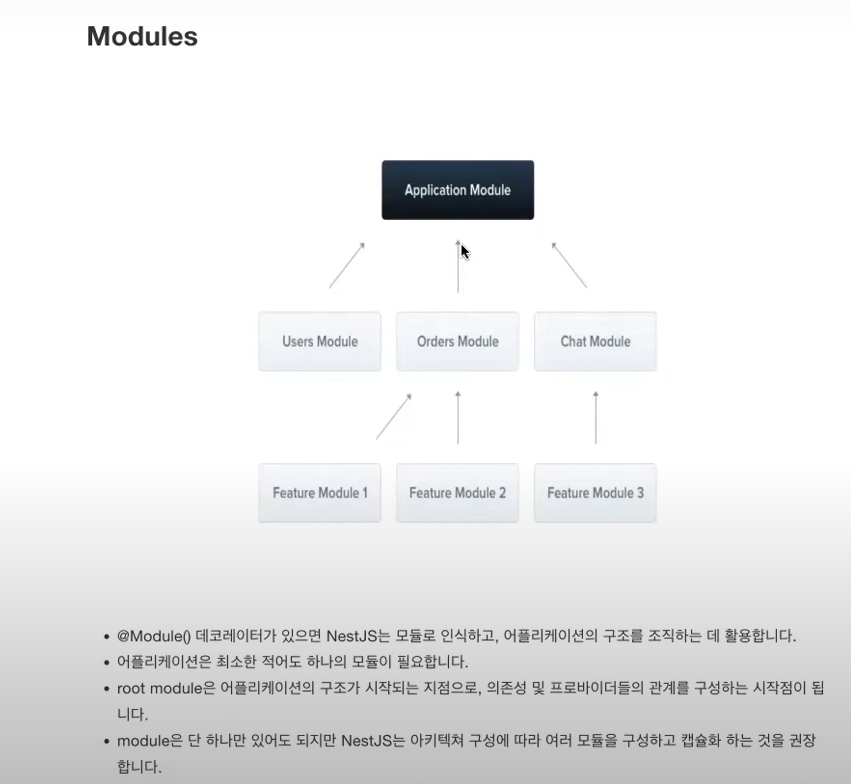
* Modules

* Feature modules

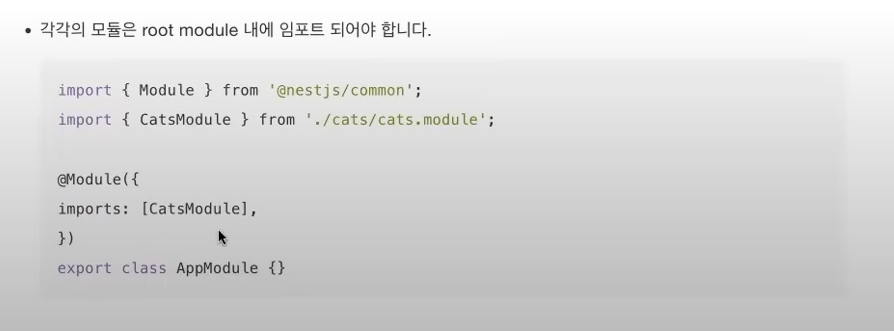
* Shared modules


* Module re-exporing

* Dependency injection (보통 사용 많이 안함)
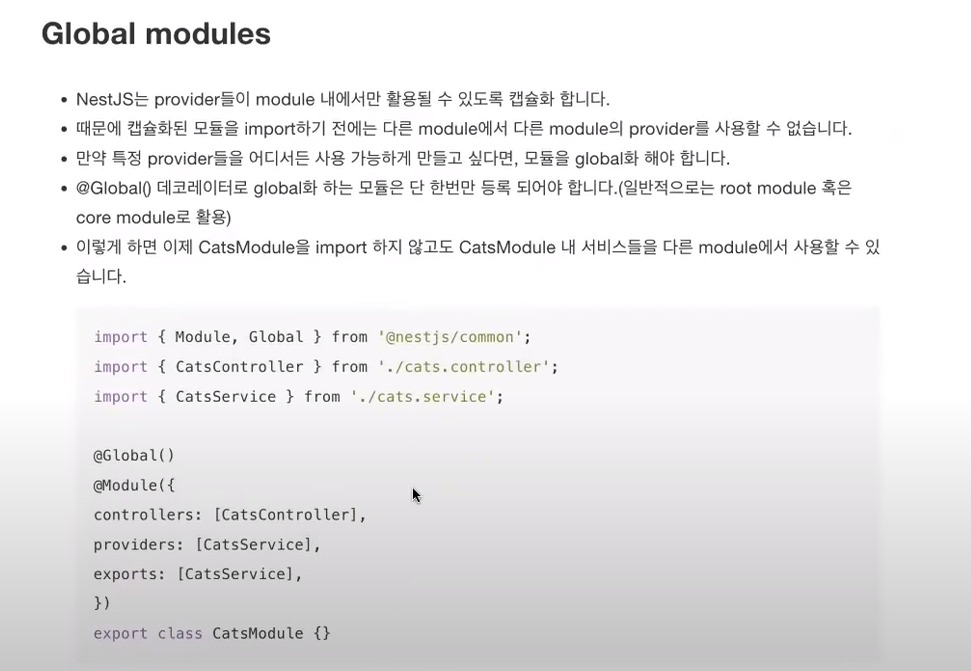
* Global Modules
* Dynamic modules

--------------------------------------------------------------------------------Module 끝
** Middleware

* Applying middleware

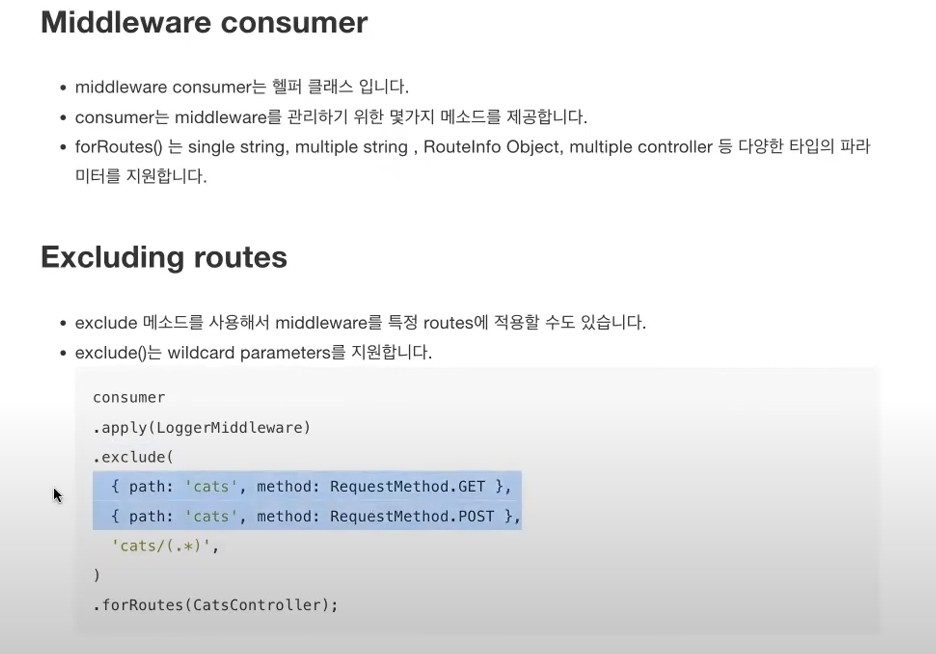
* Middleware consumer
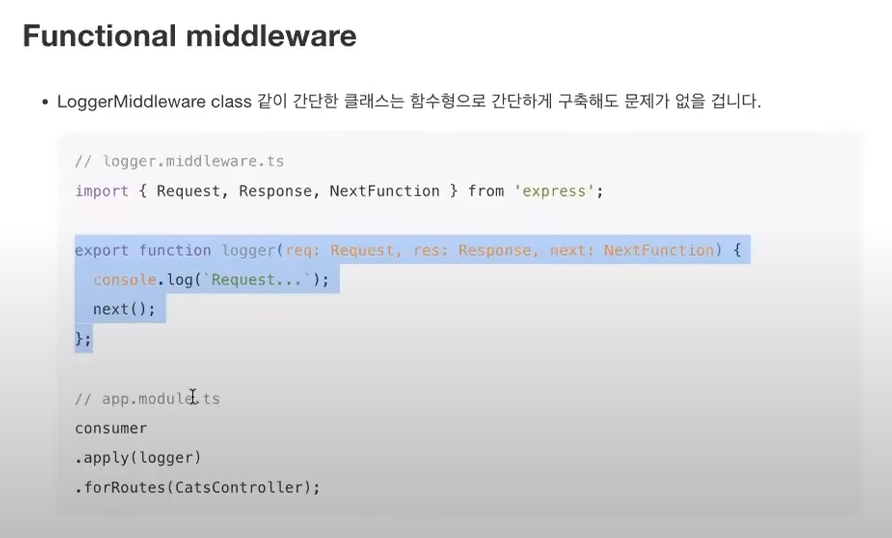
* Functional middleware
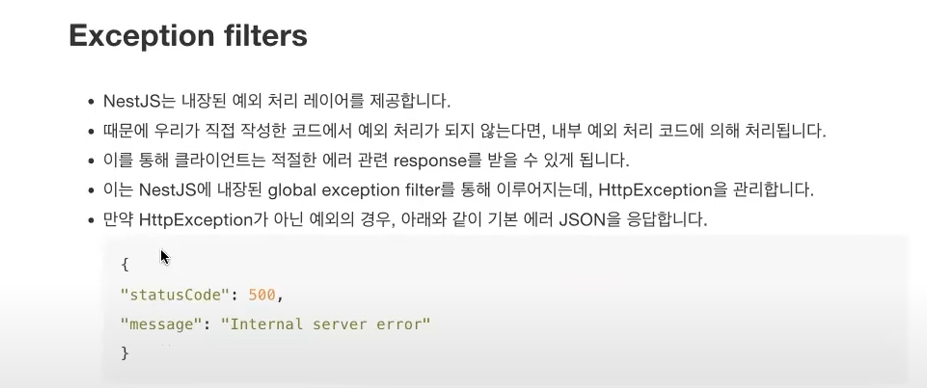
* Exception filters
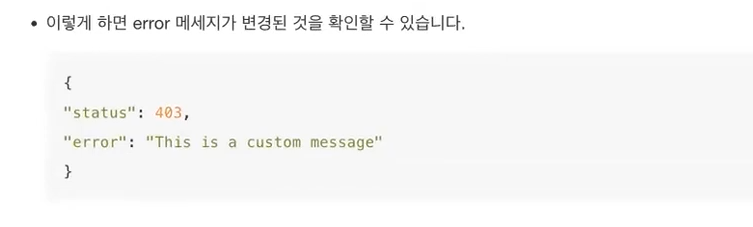
* Throwing standard exceptions

--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
** Simple API 생성

* Nest generate (링크 참조)
* bcrypt 란? (링크 참조)
- 단방향 암호화를 위해 만들어진 해시 함수로서 현업에서 가장 많이 사용되는 패스워드 암호화 알고리즘
* bcrypt 사용 이유? (단방향 암호화 이유?)
- 많은 사용자들은 동일한 ID와 Password를 여러 애플리케이션에서 사용하기에 서버 DB에 암호화 없이 비밀번호를 저장하여 보이게하면 외부적, 내부적으로 둘 다 보안 위험이 발생
- 따라서 비밀번호 암호화를 위해 해시 함수 및 Bcrypt 도입
- 암호화 자체로 데이터의 유출을 막지는 못하지만 데이터에 담긴 정보를 알 수 없게 하는 것이 목적
* bcrypt 구조
- Algorithm : 알고리즘 식별자로서 bcrypt를 의미
- Cost Factor : 키 스트레칭을 한 횟수로서 총 2^n 번인데 그 중 n 숫자를 표시
- Salt : 128 비트로 고정된 솔트값으로 22자의 base64로 인코딩된 값
- Hash : Salting & 키 스트레칭 후의 해시 값
* bcrypt 사용법
터미널
npm i --save bcrypt
* nest js swagger (https://docs.nestjs.com/openapi/introduction)
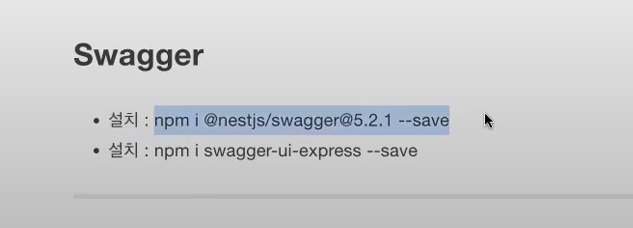
사이트에서 업데이트 된 상태로 입력하면 됨 ( 아래 사진 내용 + swagger-ui-express도 추가로 설치하기)
최신:
npm install --save @nestjs/swagger
npm install swagger-ui-express
이어서
main.tsJS
import { NestFactory } from '@nestjs/core';
import { SwaggerModule, DocumentBuilder } from '@nestjs/swagger';
import { AppModule } from './app.module';
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
const config = new DocumentBuilder()
.setTitle('Cats example')
.setDescription('The cats API description')
.setVersion('1.0')
.addTag('cats') -----------------------------<< localhost:3000/api에서 표기되는 이름
.build();
const document = SwaggerModule.createDocument(app, config);
SwaggerModule.setup('api', app, document);
await app.listen(3000);
}
bootstrap();
* Default부분 없애기
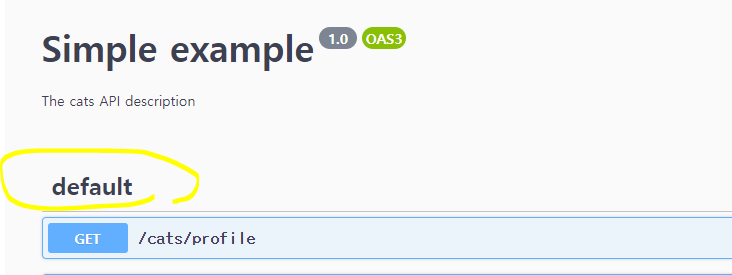
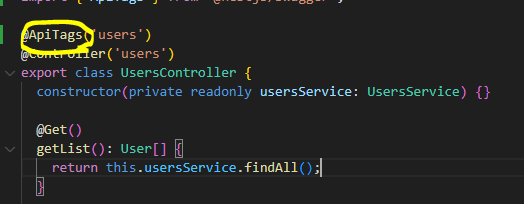
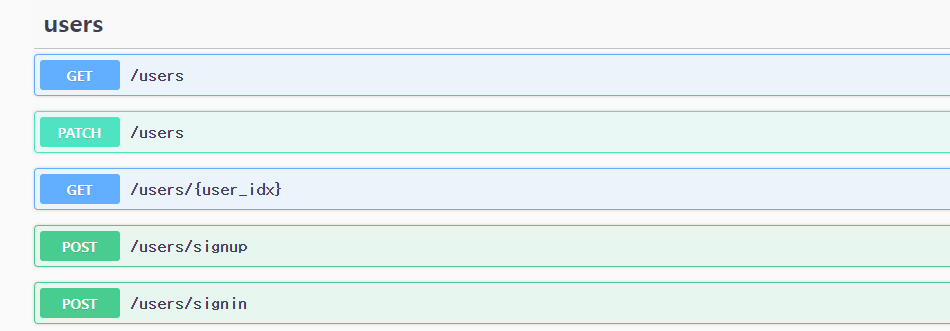
=> 그 외에 swagger에 남아있는 default들은 app.controller.ts에 남아있는 사용하지않는 코드가 남아있어서임
=> 남아있는 코드를 주석처리하면 없어짐
* nest js CRUD 생성
nest g res goods << goods는 폴더 이름임
* 괄호 안에 +id => +를 앞에 넣으면 숫자라는 의미로 사용.
@Get(':id')
findOne(@Param('id') id: string) {
return this.goodsService.findOne(+id);
}
** 배열의 길이 구하기
만약 const users = [1,2,3] 이라면
users.length는 3이 됨.
** TypeORM
: mysql이나 oracle같은 데이터베이스를 다루기 위해서는,
실제로 Query문을 작성을 해야되는데, 이러한 Query문을 함수로 대신 제공을 해서
간단하게 DB와 연동을 할 수 있는 툴
- TypeORM Integration 아래에 입력해야되는 코드 다시 작성함
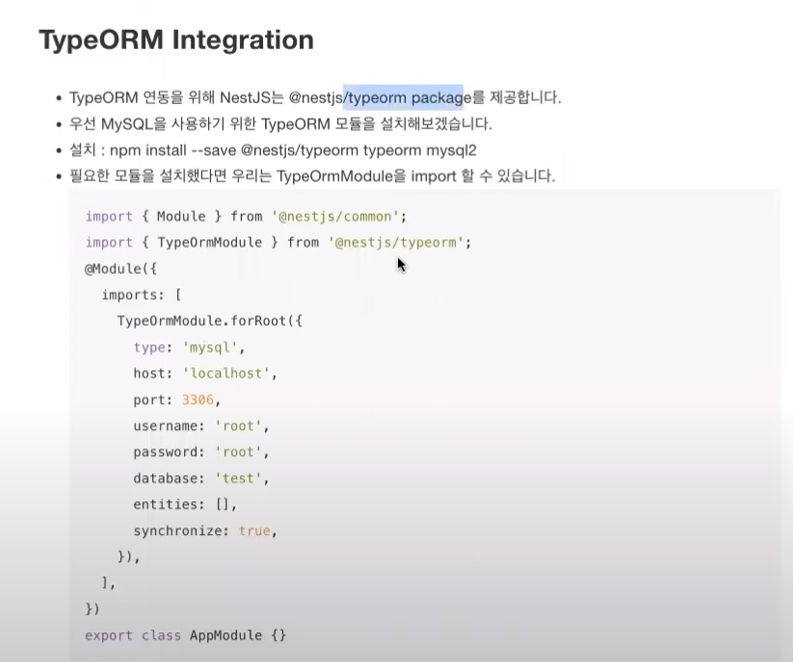

* typeorm 실행 순서
터미널에서 폴더 만들기
nest new typeorm-sample
(typeorm-sample은 예시 디렉토리임)app.module.ts에 아래 내용 추가하기
@Module({
imports: [TypeOrmModule.forRoot({
"type": "mysql",
"host": "localhost",
"port": 3306,
"username": "myname",
"password": "password1234!",
"database": "myDatabase",
entities: [],
"synchronize": false, --- 상용서버에서는 true로 하면 안 됨.
}),
UsersModule, GoodsModule],
controllers: [AppController],
providers: [AppService],
})
export class AppModule {}
* Repository pattern (https://docs.nestjs.com/techniques/database#repository-pattern)
바로 아래에 코드는 따로 작성함
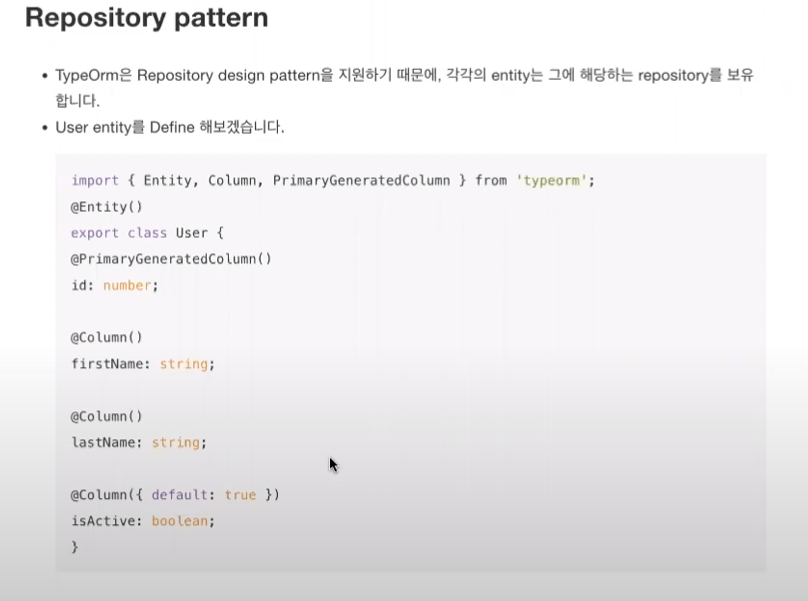
users.entity.ts 폴더를 하나 만들어서,
아래 내용들은 붙여넣기
import { Entity, Column, PrimaryGeneratedColumn } from 'typeorm';
@Entity()
export class User {
@PrimaryGeneratedColumn()
id: number;
@Column()
firstName: string;
@Column()
lastName: string;
@Column({ default: true })
isActive: boolean;
}
* Entity
app.module.ts의 entities: [ ] 대괄호 안에 class명 넣어주기
entities: [User]
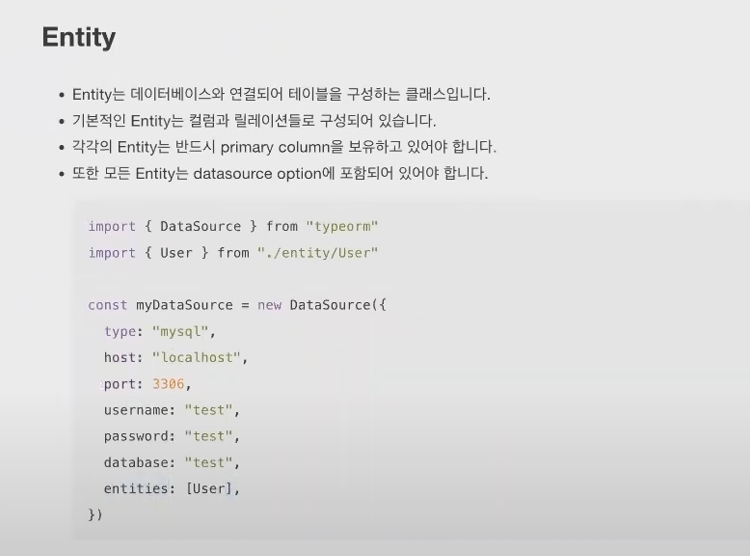
* Mysql workbench 통해서 DB랑 연결하기
app.module.ts
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { AppController } from './app.controller';
import { AppService } from './app.service';
import { TypeOrmModule } from '@nestjs/typeorm';
import { User } from 'src/users/entities/user.entity';
import { UsersModule } from 'src/users/users.module';
import { GoodsModule } from 'src/goods/goods.module';
@Module({
imports: [
UsersModule,
GoodsModule,
TypeOrmModule.forRoot({
type: 'mysql',
host: 'localhost',
port: 3306,
username: 'root',
password: '1234',
database: 'nestjs-db', --- myworkbench에 접속해서 만든 폴더 이름임
entities: [User],
synchronize: true,
}),
],
controllers: [AppController],
providers: [AppService],
})
export class AppModule {}
* Entity 이어서 내용임
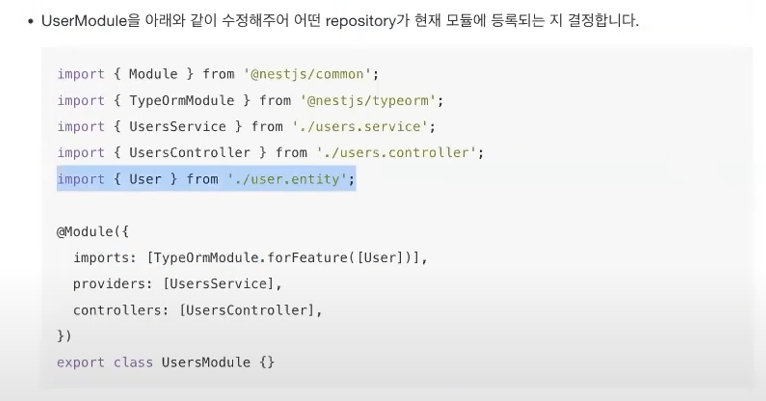
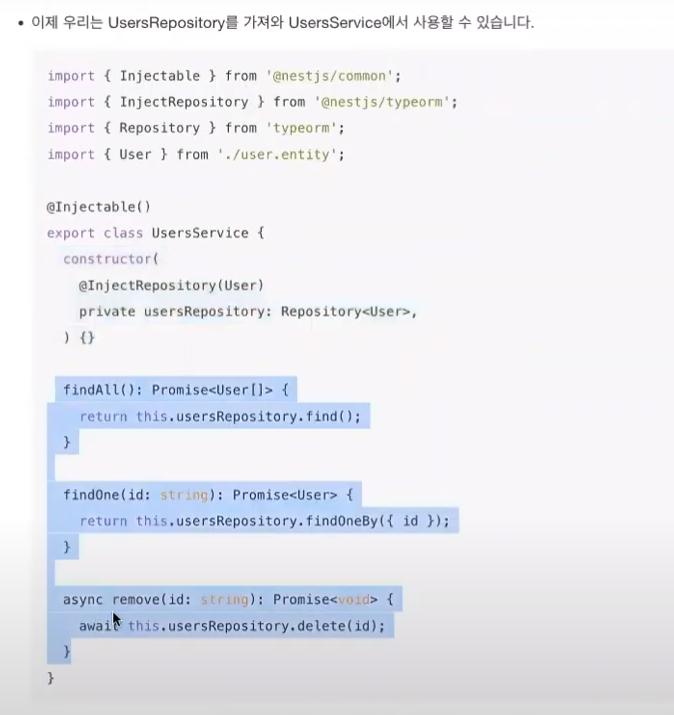
* App.module.ts의 entities부분에 [ User ]를 넣어주고,
users.module.ts에 import해줌으로써, user부분에서도 entity를 사용할 수 있게됨.
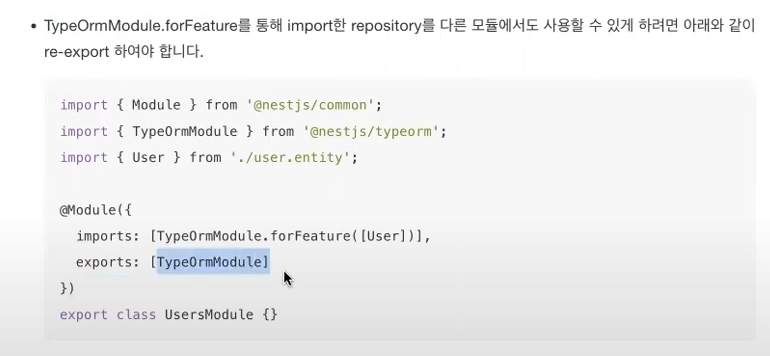
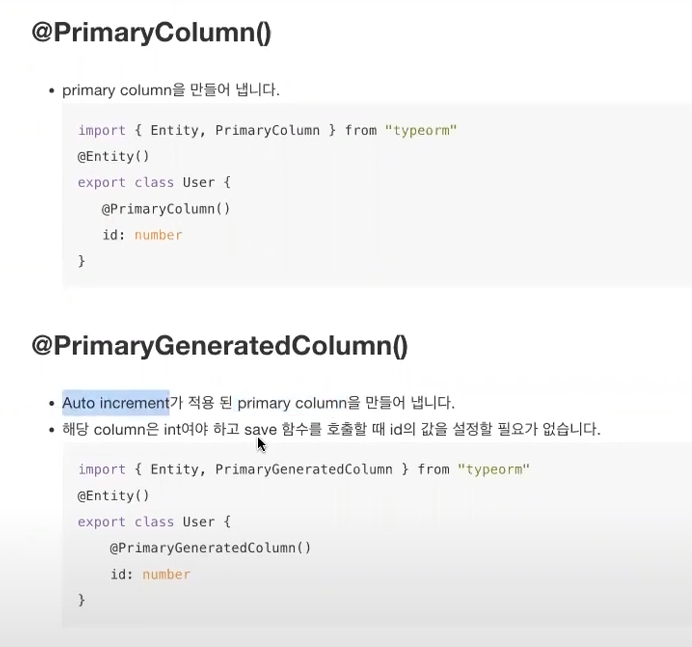
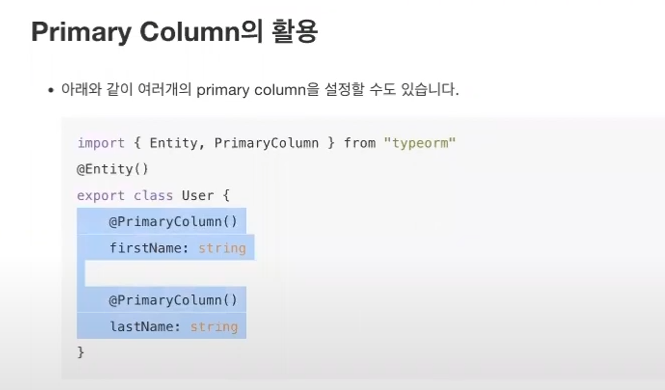
* PrimaryColumn()
Auto increment를 가장 많이 사용함
* uuid로 하고싶다면
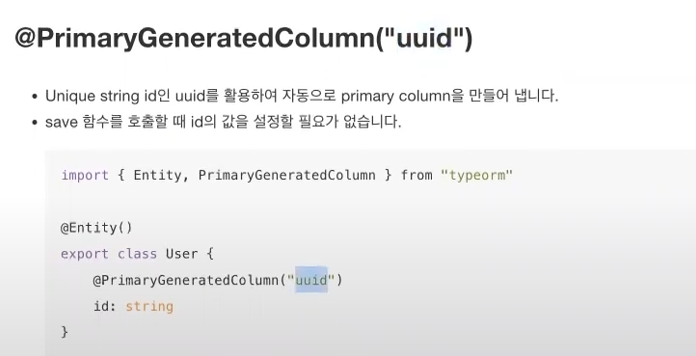
* Primary Column 활용
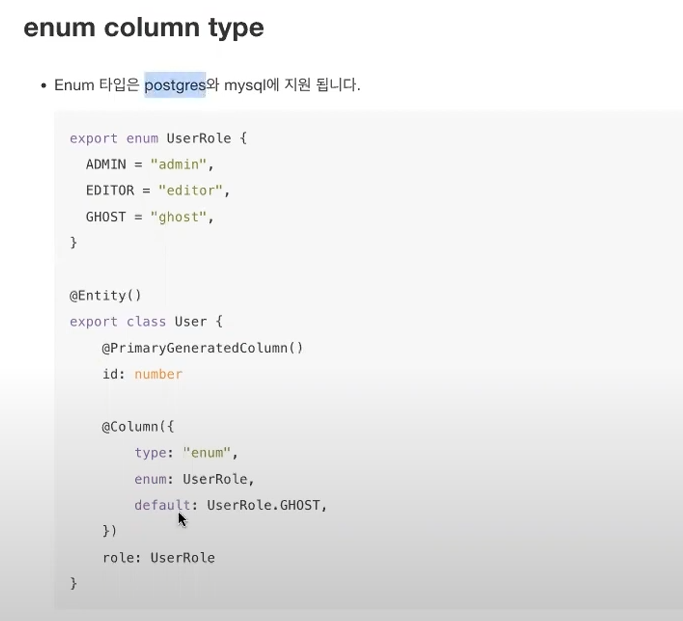
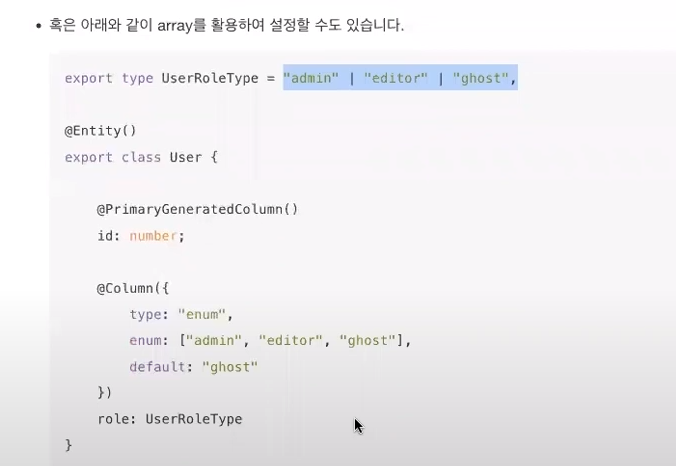
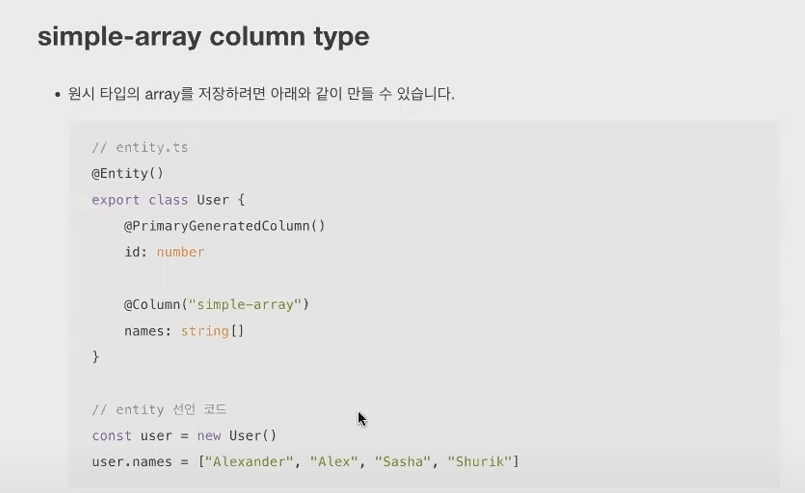
* enum column type

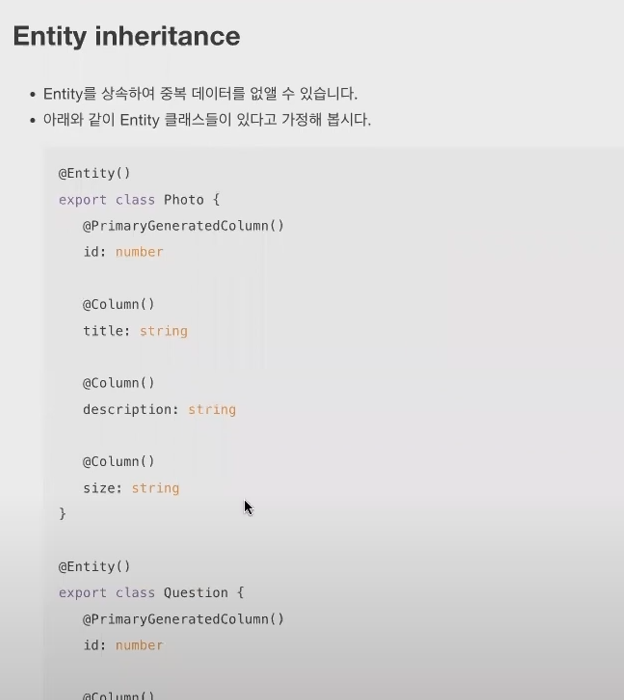
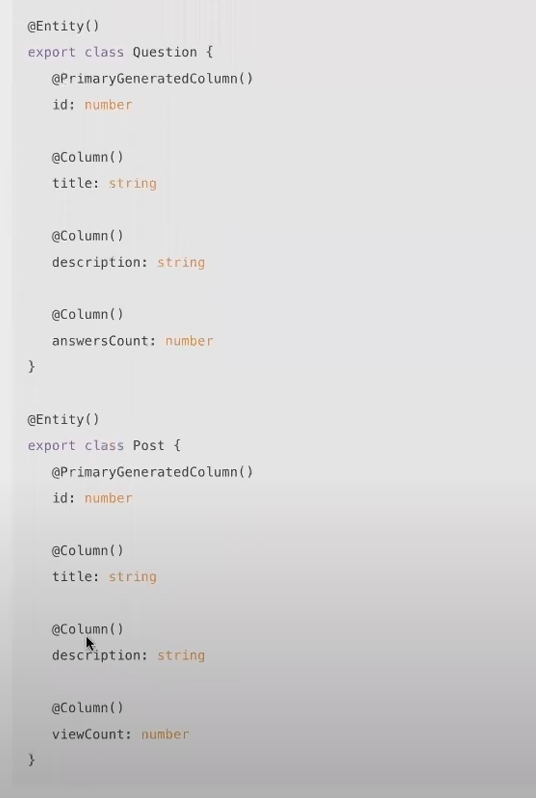
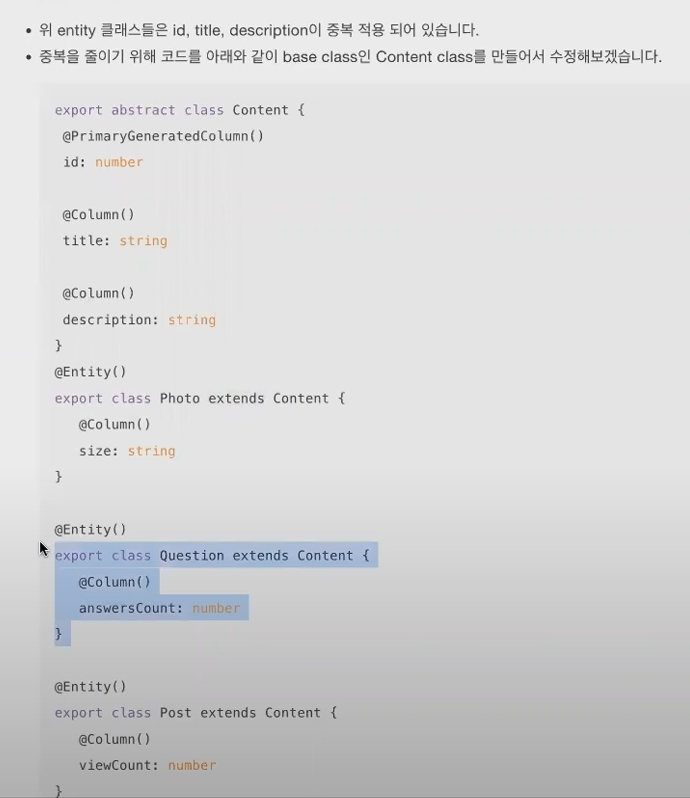
* Entity inheritance
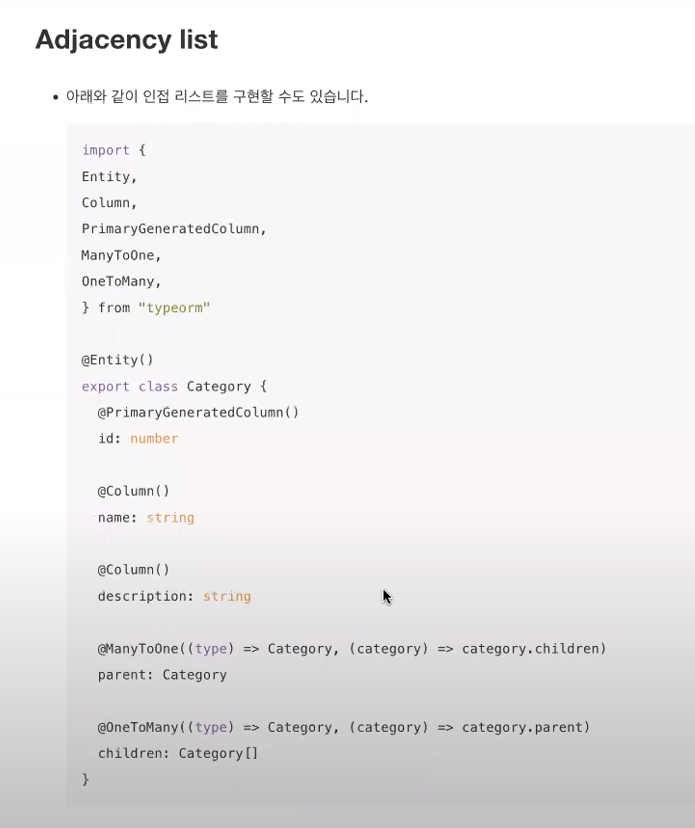
* Adjacency list
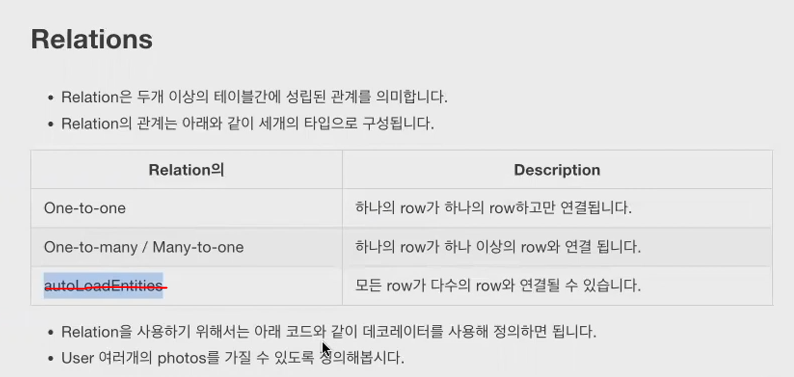
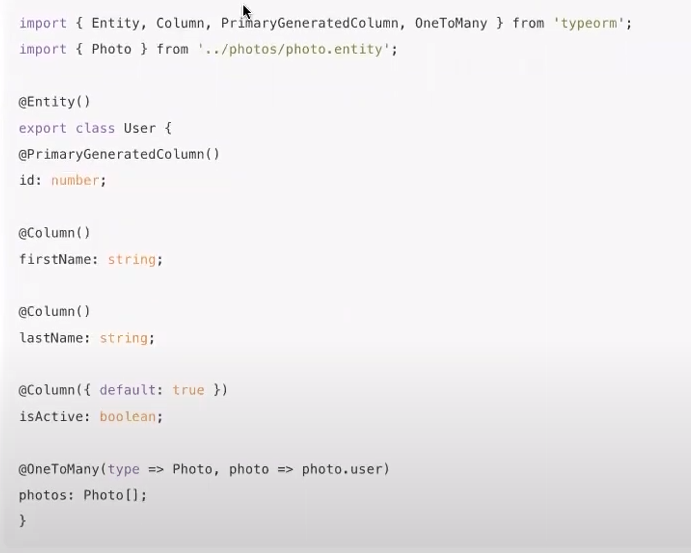
* Relations
빨간색 점선부분 many to many임
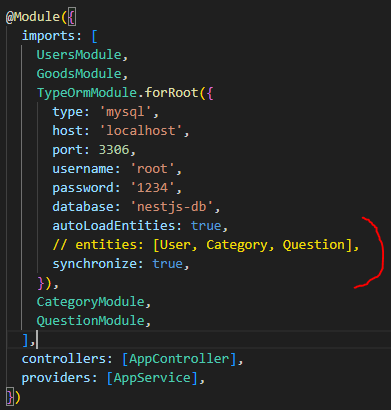
* Auto-load entites

위처럼 설정을 하면, app.module.ts에서 entities: [User, Category, Question] 이런식으로 작성 안해도 자동으로 등록이 됨.
* Transactions

users.service.ts
@Injectable()
export class UsersService {
constructor(
private dataSource: DataSource,
) {}
}
- 그 다음에는 transaction을 위한 object를 만듭니다.
users.service.ts
async createMany(users: User[]) {
const queryRunner = this.dataSource.createQueryRunner();
await queryRunner.connect();
await queryRunner.startTransaction();
try {
await queryRunner.manager.save(users[0]);
await queryRunner.manager.save(users[1]);
await queryRunner.commitTransaction();
} catch (err) {
// since we have errors lets rollback the changes we made
await queryRunner.rollbackTransaction();
} finally {
// you need to release a queryRunner which was manually instantiated
await queryRunner.release();
}
}

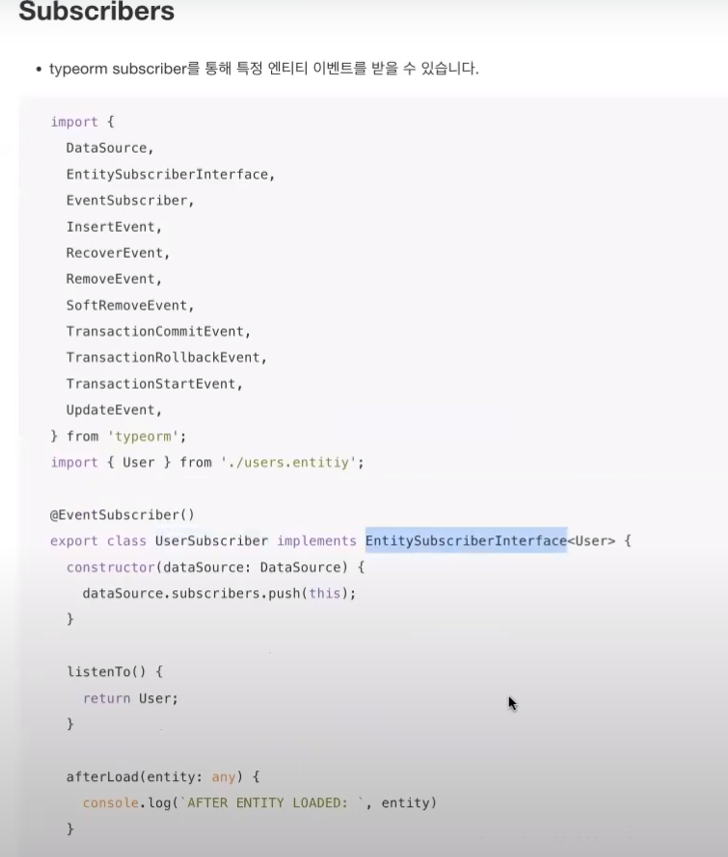
* Subscribers (section 3 / 1:03 )
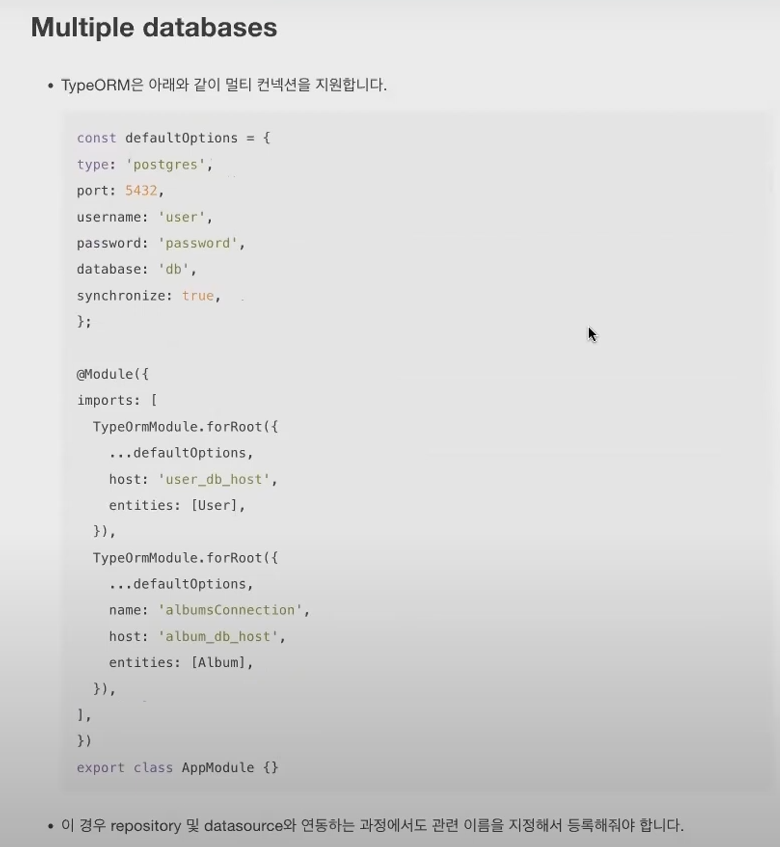
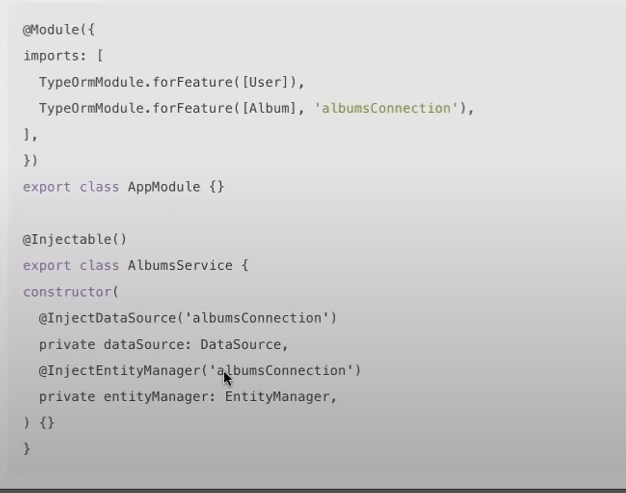
* Multiple databases
* Authentication(인증, 보안 관련)
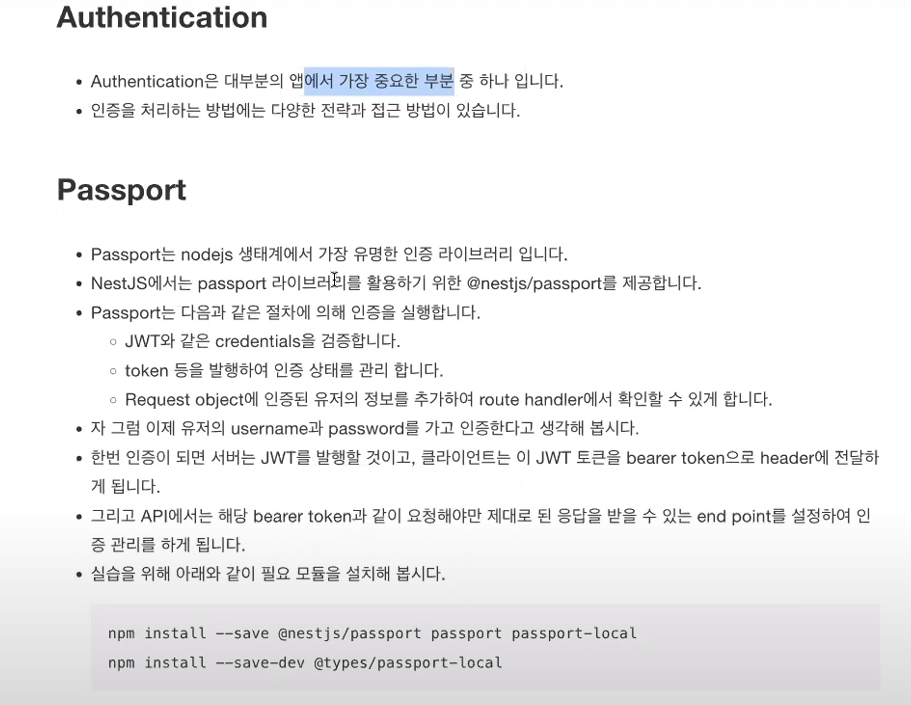
npm install --save @nestjs/passport passport passport-local
npm i --save-dev @types/passport-local
* 인증 구현

nest g module auth
nest g service auth
* user service 코드에 아래와 같은 예제 코드를 추가해보기
private readonly users [
{
userId: 1,
username: 'john',
password: 'changeme',
},
{
userId: 2,
username: 'maria',
password: 'guess',
},
];
async findOne(username: string): Promise<User | undefined> {
return this.users.find(user => user.username === username);
}
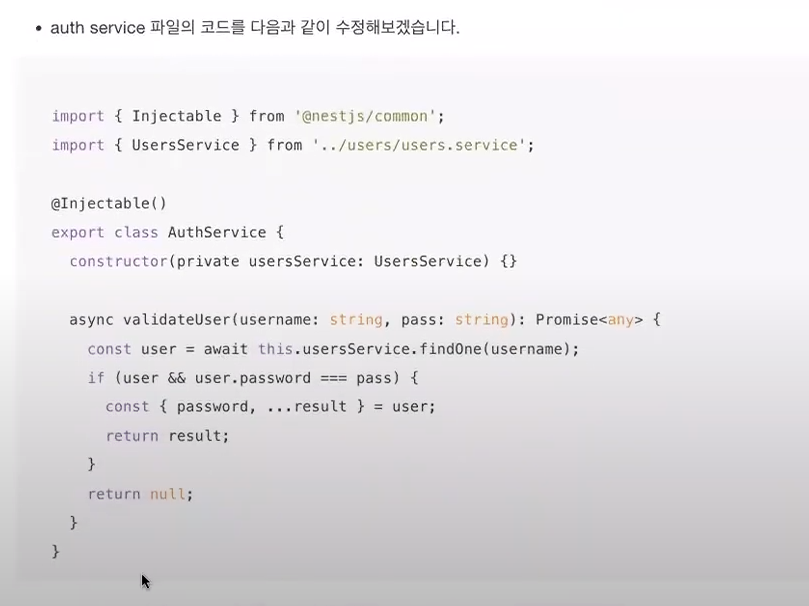
import { UsersService } from './../users/users.service';
import { Injectable } from '@nestjs/common';
@Injectable()
export class AuthService {
constructor(private usersService: UsersService) {}
async validateUser(username: string, pass: string): Promise<any> {
const user = await this.usersService.findOne(username);
if (user && user.password === pass) {
const { password, ...result } = user;
return result;
}
}
}

* auth. module에서
@Module({
imports: [UsersModule],
providers: [AuthService, UsersService],
})
export class AuthModule {}
* Passport local
import { Strategy } from 'passport-local';
import { PassportStrategy } from '@nestjs/passport';
import { Injectable, UnauthorizedException } from '@nestjs/common';
import { AuthService } from './auth.service';
@Injectable()
export class LocalStrategy extends PassportStrategy(Strategy) {
constructor(private authService: AuthService) {
super();
}
async validate(username: string, password: string): Promise<any> {
const user = await this.authService.validateUser(username, password);
if (!user) {
throw new UnauthorizedException();
}
return user;
}
}
* Passport local

auth/local.strategy.ts
import { Strategy } from 'passport-local';
import { PassportStrategy } from '@nestjs/passport';
import { Injectable, UnauthorizedException } from '@nestjs/common';
import { AuthService } from './auth.service';
@Injectable()
export class LocalStrategy extends PassportStrategy(Strategy) {
constructor(private authService: AuthService) {
super();
}
async validate(username: string, password: string): Promise<any> {
const user = await this.authService.validateUser(username, password);
if (!user) {
throw new UnauthorizedException();
}
return user;
}
}
auth/auth.module.ts
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { AuthService } from './auth.service';
import { UsersModule } from '../users/users.module';
import { PassportModule } from '@nestjs/passport';
import { LocalStrategy } from './local.strategy';
@Module({
imports: [UsersModule, PassportModule],
providers: [AuthService, LocalStrategy],
})
export class AuthModule {}
* Built-in Passport Guards

* Login route

users.controller.ts
@UseGuards(AuthGuard)
@Post('auth/login')
async login(@Request() req) {
return req.user;
}

* 여기까지 passport와 built-in guard를 활용한 validate 코드의 기본적인 작동 방법을 알아 보았음.
* JWT

npm i --save @nestjs/jwt passport-jwt
npm i --save-dev @types/passport-jwt
auth/auth.service.ts
import { Injectable } from '@nestjs/common';
import { UsersService } from '../users/users.service';
import { JwtService } from '@nestjs/jwt';
@Injectable()
export class AuthService {
constructor(
private usersService: UsersService,
private jwtService: JwtService
) {}
async validateUser(username: string, pass: string): Promise<any> {
const user = await this.usersService.findOne(username);
if (user && user.password === pass) {
const { password, ...result } = user;
return result;
}
return null;
}
async login(user: any) {
const payload = { username: user.username, sub: user.userId };
return {
access_token: this.jwtService.sign(payload),
};
}
}

auth/constants.ts
export const jwtConstants = {
secret: 'DO NOT USE THIS VALUE. INSTEAD, CREATE A COMPLEX SECRET AND KEEP IT SAFE OUTSIDE OF THE SOURCE CODE.',
};

auth/auth.module.ts
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { AuthService } from './auth.service';
import { LocalStrategy } from './local.strategy';
import { UsersModule } from '../users/users.module';
import { PassportModule } from '@nestjs/passport';
import { JwtModule } from '@nestjs/jwt';
import { jwtConstants } from './constants';
@Module({
imports: [
UsersModule,
PassportModule,
JwtModule.register({
secret: jwtConstants.secret,
signOptions: { expiresIn: '60s' },
}),
],
providers: [AuthService, LocalStrategy],
exports: [AuthService],
})
export class AuthModule {}

users.controller
user/auth/login route의 코드도 변경
@UseGuards(LocalAuthGuard)
@Post('auth/login')
async login(@Request() req) {
return this.authService.login(req.user);
}
}
